After a decade-long wait, India will finally implement the GST tax system. It is expected that GST can boost GDP growth 1.5 to 2 percentage. This is the biggest tax and economic reform which will change completely business process in the country. GST will help remove tax barriers between states, creating a “one nation one tax” concept. The roll-out will replace of cascading effect of central, state, interstate and local (mostly) taxes with a single, nationwide, value-added tax (GST) on goods and services.
Recently, ACG reviewed the Indian Automobile Industry forecast after implementation of GST model.
ACG Premium subscribers contact us to get this report since this report is part of subscription package or Contact to the become premium subscriber.
The purpose of introducing GST model is one single tax on supply of goods and services, from the manufacturer to the final consumer. This model will replace all indirect taxes and only GST will be applied as an indirect tax. As a result, it avoids the cascading effect which raises the tax burden on the end consumer. The credit of input taxes will be paid at each stage which will be available in the succeeding stage of value addition.
The final consumer of the goods and/or services will only have to bear the GST charged by the final dealer in the end to end supply chain, and avail set-off benefits at all the previous stages. This means all indirect tax will be engaged under GST.
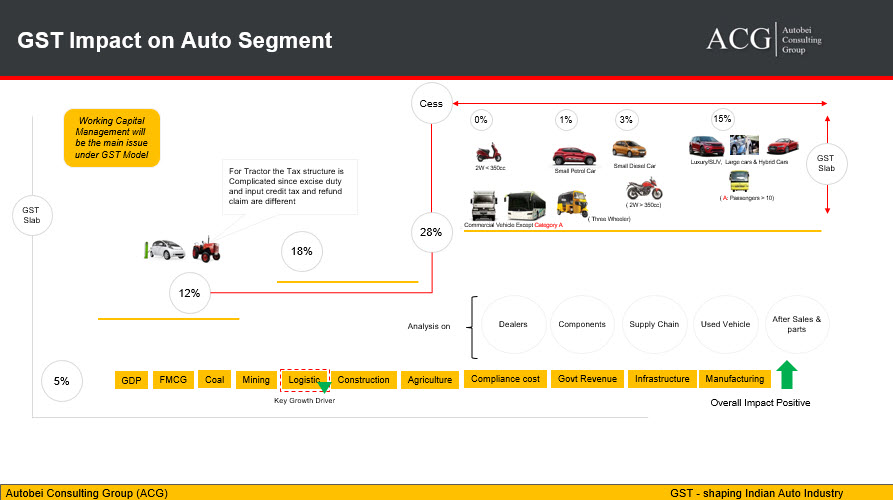
GST will give new shape to Indian Automobile Industry. Our detail study describes the current business practice, Market dynamics and how GST will make an impact on all attributes of Industry.The majority of the Automobile verticals are coming under 28 percent tax slab except for Electric Vehicle and Tractor.
To draw the conclusion of its impact, we have to analyze not only the accounting practice but also see a larger picture of its effects on all Industry after implementation of a new tax system. The change will be beneficial for Industry along with some challenges in an initial stage. The new tax system will have an impact on the complete supply chain of Industry – start with Suppliers, Manufacturer, Distributor, Logistic model, and Dealers.
All components of this chain will have contribution at different stage and level. We have analyzed their impact on Sales, Production, Export, Components business model, their logistic cost, Vehicle logistic practice from plant to warehouse to Dealers.
In simple term, we cannot just see the accounting number change on price, Tax on material cost, and expenses but also need to research on other industry and its impact on Auto Industry.
According to the current tax system, when companies move their goods from one State to another and selling it in the other State, then they are liable to pay 2 Percent CST on Value of goods and Excise duty. To avoid this tax, company transfer the stock to another state to their warehouse since there is no tax on the stock transfer. Since most of the Automobile OEMs sell their 70 to 80 percent product in other state and produce goods in the only specific state. As a result, currently OEMs have warehouses within every State and move their goods as stock transfer and then sales to their dealers. In this practice, there is additional cost come which finally customers have to pay. With GST Business model in, companies will be freed from this problem and they can sell directly to dealers under IGST tax.
Since the logistic cost of any goods transportation is going to reduce by 25 to 35%, the will increase the consumption of goods and increase demand.
Impact on Sale: There is a different scenario and it depends on an Auto segment like a Small Petrol car, Small Diesel Car, Sedan, Sports, Luxury Vehicle, Truck, Bus – Seating capacity, Two-Wheeler – Engine CC, Tractor or Construction Equipment. We have analyzed all these verticals in detail.
Auto Component is also playing important role in Auto Industry. They are the first who start the manufacturing chain. After GST, organized and unorganized will be on the same platform since both would have to follow compliances and will drive competitiveness for the organized segment. The OEM will get input tax credit only if a vendor will be registered under GST regime. This will reduce the end product cost also.
The common business practice of auto component companies has been setting up plant close to the OEM factories. There is two key reason of this strategy: Just-in-time supplies, cost-effective business model, and current tax system.
There are two ways how the supply chain works from Auto ancillary to the end dealer via OEM.
Modified aftermarket distribution models: The GST can have a big impact on the spares aftermarket because of increasing requirements for storage and retail penetration. GST defined how to calculate tax if the service and parts both are providing by dealers to customers. Since the parts are coming under 28% tax slab, there could be some negative impact work on it.
Impact on Import and Export: There is a positive impact on export, now tax will be not exported, only goods will be exported. Under GST model imported tax is going to increase and there will tough competition with local manufacturer products.
Major Challenge: During the transition process, there will be a major impact on working capital. The earlier assessment of working capital requirement is going to be changed. We are having key expertise in working capital management. Since GST process is available via an online tool, all forms need at least basic IT infrastructure and computer skills to deal with GST. This is close to Digital India concept.
Make in India: GST system is designed in such a way that it promote make in India concept.